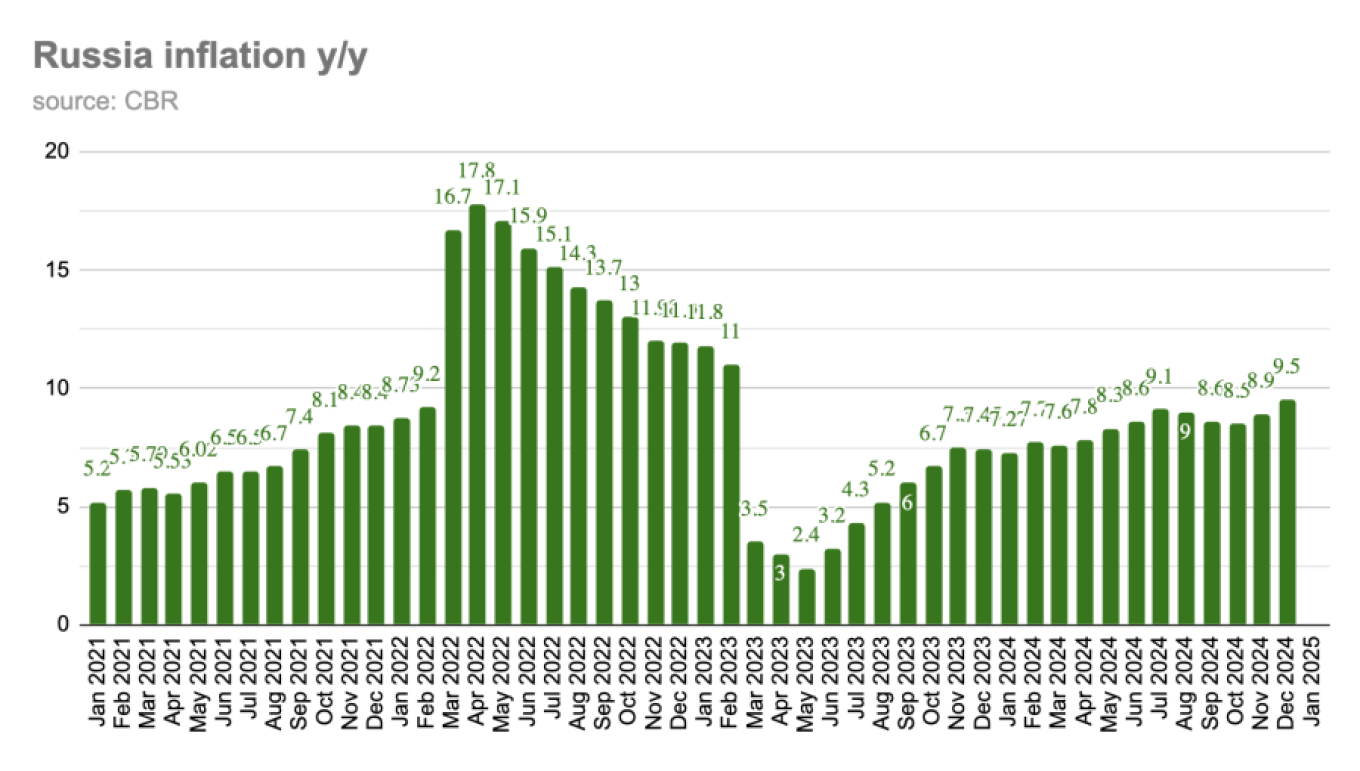
Russias runaway consumer price inflation (CPI) made more gains in December, rising to 9.5% y/y, as the Central Bank continues to lose the fight to reign in rising prices.The rise in Russian inflation to 9.5% y/y in December is likely to be followed by an increase to more than 10% early this year.
The Central Bank has set a high bar for further tightening but we think the balance remains tilted towards another interest rate hike this quarter, Liam Peach, the senior emerging market economist with Capital Economics, said in a note.Inflation started to climb in the second quarter of 2023 and Central Bank Governor Elvia Nabiullina reversed a previous easing policy and has been increasing rates ever since in a futile attempt to halt the price rises.
In a surprise decision in December, the Central Bankleft rates on hold at 21%their highest level in years as theCentral Bank comes under increasing pressure to cut rates that havedriven borrowing costs up to a very painful level.Inflation rose from 8.9% y/y in November to 9.5% last month but was a bit softer than the consensus (for 9.7%) but prices rose by a chunky 1.3% in month-on-month terms, Capital Economics reports.Russias inflation is out of control.
In December, prices accelerated again, up 9.5% despite crushingly high interest rates of 21%.
The problem is inflation is being driven by massive $100 billion a year of military spending, something that the Central Bank is powerless to reduce.bne IntelliNewsAll components increased, with food inflation surging from 9.9% y/y in November to 11.1%, services rising from 11.4% y/y to 11.5% and non-food goods up from 5.7% y/y to 6.1%.
Core inflation came in at 1.0% m/m which, over the fourth quarter as a whole, is equivalent to around 10% in seasonally adjusted annualized terms according to Capital Economics estimates.The problem is that traditional monetary policy tools to bring down inflation dont work as the cause of the inflation is not problems with money supply, but the fact that the Kremlin has pumped some 10 trillion rubles ($100 billion) in military spending in 2024 a source of money that the Central Bank is powerless to limit.
The upshot is that Russias economy, which grew by an estimated 4% last year, is overheated and running well ahead of its potential growth of around 1.5%.The problem has been exacerbated by additional off-budget spending.
According to a recent report from the Davis Center at Harvard University, the Kremlin has also forced banks to make state-direct soft loans to defense companies to the tune of 25 trillion rubles ($250 billion), which has added to the torrent of cash pouring into the system.
The Davis Center warned of a loomingcredit crisisunless this lending is curtailed.
However, other economists say theRussian economy is more robust than first appearsand the chance of a crisis remains low.A testament to the size of the problem is the enormous spread of 11.5% between interest rates and inflation, the real interest rate, an unprecedented level in traditional monetary policy.
According tobne IntelliNewsestimates, given Russias growth rate in 2024 and the Central Banks 4% inflation target, Russias interest rates should be cut by 450 basis points to 16.5%, according to the Taylor rule, an economic tool for estimating the appropriate prime interest rate level.Last fall, the Central Bank teamed up with the Finance Ministry to usenon-monetary policy methodsto reduce corporate borrowing and bring down inflation that way.
And asbne IntelliNewsreported, corporate lending did begin to slow in the last two months of 2024, although the pace has been too slow to impact inflation so far, the latest results show.The unexpected decision by Russias Central Bank to leave its policy rate on hold at 21.00% in December, rather than hike as most expected, suggests that there is a high bar for further tightening, says Peach.
The Central Bank commented on the recent softening in credit growth as one reason why it paused.
For now, we dont expect another rate hike.
But inflation is out of control and we think the bias will remain towards further monetary tightening in the coming months as inflation continues to rise and inflation expectations remain elevated.This article was originally published by bne IntelliNews.

 12
12







