INSUBCONTINENT EXCLUSIVE:
At its annual TechCon event in San Jose, Arm today announced Custom Instructions, a new feature of its Armv8-M architecture for embedded
CPUs that, as the name implies, enables its customers to write their own custom instructions to accelerate their specific use cases for
embedded and IoT applications.
We already have ways to add acceleration, but not as deep and down to the heart of the CPU
What we&re giving [our customers] here is the flexibility to program your own instructions, to define your own instructions — and have
them executed by the CPU,& ARM senior director for its automotive and IoT business, Thomas Ensergueix, told me ahead of today
announcement.
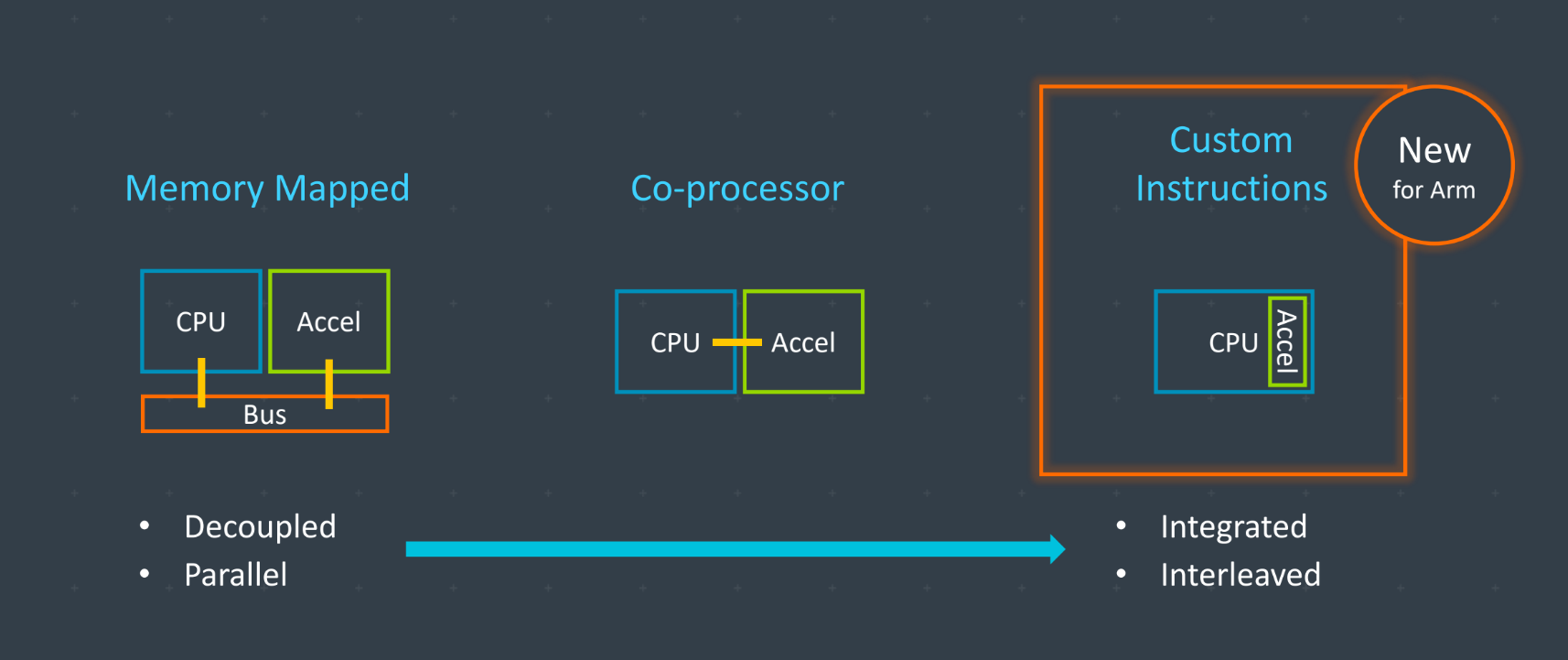
He noted that Arm always had a continuum of options for acceleration, starting with its memory-mapped architecture for
connecting over a bus GPUs and today neural processor units
This allows the CPU and the accelerator to run in parallel, but with the bus being the bottleneck
Customers also can opt for a co-processor that directly connected to the CPU, but today news essentially allows Arm customers to create
their own accelerated algorithms that then run directly on the CPU
That means the latency is low, but it not running in parallel, as with the memory-mapped solution.
As Arm argues, this setup allows for
the lowest-cost (and risk) path for integrating customer workload acceleration, as there are no disruptions to the existing CPU features and
it still allows its customers to use the existing standard tools with which they are already familiar.
For now, custom instructions will
only be available to be implemented in the Arm Cortex-M33 CPUs, starting in the first half of 2020
By default, it&ll also be available for all future Cortex-M processors
There are no additional costs or new licenses to buy for Arm customers.
Ensergueix noted that as we&re moving to a world with more and more
connected devices, more of Arm customers will want to optimize their processors for their often very specific use cases — and often
they&ll want to do so because by creating custom instructions, they can get a bit more battery life out of these devices, for example.
Arm
has already lined up a number of partners to support Custom Instructions, including IAR Systems, NXP, Silicon Labs and STMicroelectronics
.
Arm new Custom Instructions capabilities allow silicon suppliers like NXP to offer their customers a new degree of application-specific
instruction optimizations to improve performance, power dissipation and static code size for new and emerging embedded applications,& writes
NXP Geoff Lees, SVP and GM of Microcontrollers
&Additionally, all these improvements are enabled within the extensive Cortex-M ecosystem, so customers& existing software investments are
maximized.
In related embedded news, Arm also today announced that it is setting up a governance model for Mbed OS, its open-source
operating system for embedded devices that run an Arm Cortex-M chip
Mbed OS has always been open source, but the Mbed OS Partner Governance model will allow Arm Mbed silicon partners to have more of a say in
how the OS is developed through tools like a monthly Product Working Group meeting
Partners like Analog Devices, Cypress, Nuvoton, NXP, Renesas, Realtek,
Samsung and u-blox are already participating in this group.