INSUBCONTINENT EXCLUSIVE:
In the time of COVID-19, much of what transpires from the science world to the general public relates to the virus, and understandably so
But other domains, even within medical research, are still active — and as usual, there are tons of interesting (and heartening) stories
out there that shouldn&t be lost in the furious activity of coronavirus coverage
This last week brought good news for several medical conditions as well as some innovations that could improve weather reporting and maybe
save a few lives in Cambodia.
Ultrasound and AI promise better diagnosis of arrhythmia
Arrhythmia is a relatively common condition in which
the heart beats at an abnormal rate, causing a variety of effects, including, potentially, death
Detecting it is done using an electrocardiogram, and while the technique is sound and widely used, it has its limitations: first, it relies
heavily on an expert interpreting the signal, and second, even an expert diagnosis doesn&t give a good idea of what the issue looks like in
Knowing exactly where the flaw is makes treatment much easier.
Ultrasound is used for internal imaging in lots of ways, but two recent
studies establish it as perhaps the next major step in arrhythmia treatment
Researchers at Columbia University used a form of ultrasound monitoring called Electromechanical Wave Imaging to create 3D animations of the
patient heart as it beat, which helped specialists predict 96% of arrhythmia locations compared with 71% when using the ECG
The two could be used together to provide a more accurate picture of the heart condition before undergoing treatment.
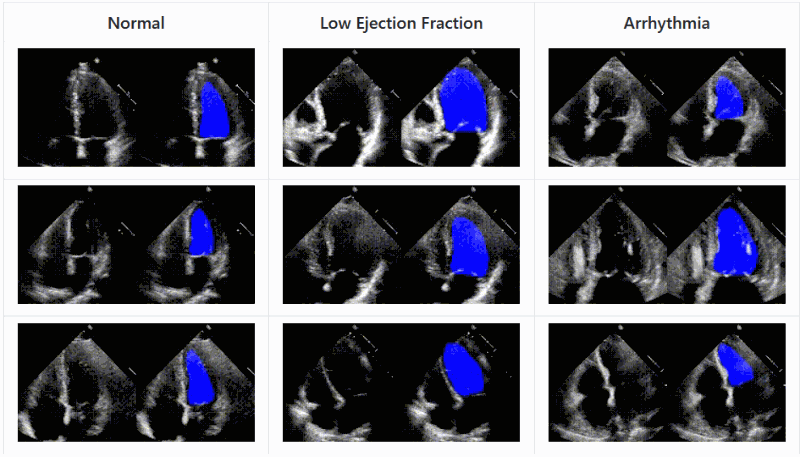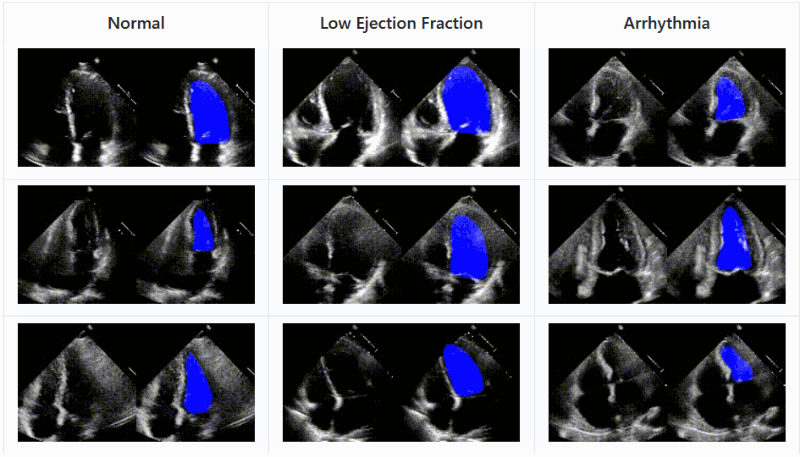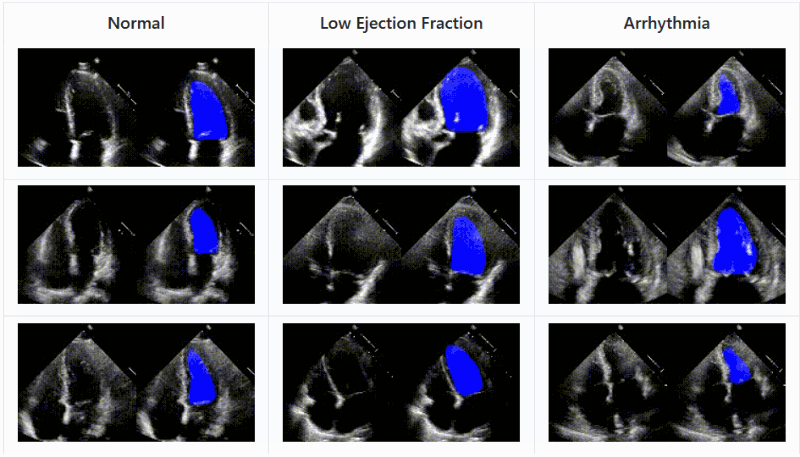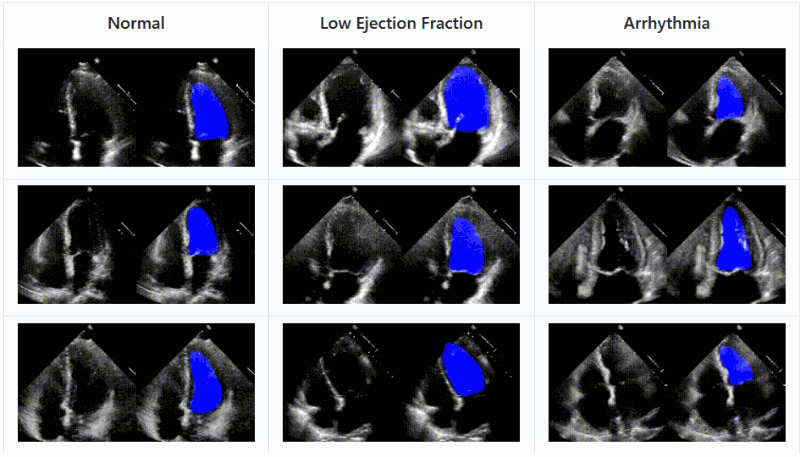
Another approach
from Stanford applies deep learning techniques to ultrasound imagery and shows that an AI agent can recognize the parts of the heart and
record the efficiency with which it is moving blood with accuracy comparable to experts
As with other medical imagery AIs, this isn&t about replacing a doctor but augmenting them; an automated system can help triage and
prioritize effectively, suggest things the doctor might have missed or provide an impartial concurrence with their opinion
The code and data set of EchoNet are available for download and inspection.